Another first from Dutypoint
ScubaTank® is now the UK’s first
EPD-Certified Booster Set
Continue to Dutypoint


Break tanks are used in pressure-boosting water systems to supply sufficient net-positive suction head (NPSH) to a pump in situations where mains water pressure is not sufficient to supply the requirements of the system. Break tanks typically feature an air gap between the inlet and maximum water level to prevent backflow.
Please note that some of the guidance in this article is based on BS EN 806 Part 2. Any further recommendations are for guidance only and should always be checked by a qualified mechanical, public health or building services engineer, as the requirements of different projects can vary greatly.

The table shows the recommended minimum storage levels for each type of premises. The likely peak occupancy of the building should be considered when making this calculation. When sizing for a domestic building, a standard property should be sized as a hostel; storage of 90 litres per person is sufficient for most installations. High-end properties may require additional storage.
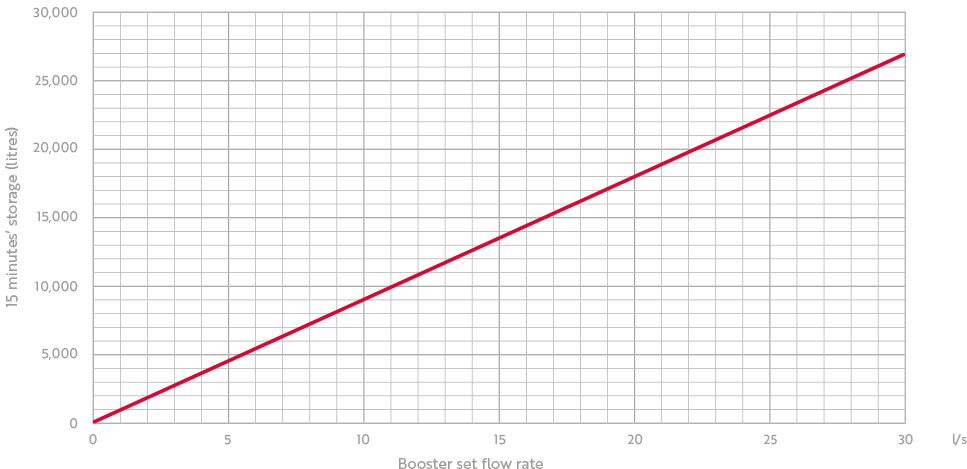
Secondly, the expected peak flow rate of the premises should be considered. The peak flow is calculated when sizing the booster set. In determining the peak flow rate, we must consider how much water storage must be provided to facilitate this flow rate. Dutypoint recommends that a minimum of 15 minutes storage, according to the peak flow rate of the booster set, should be provided in a booster set break tank within a commercial installation. For example, a booster set with a peak design flow rate of 1.1 litres/second or 66 litres/minute requires a break tank with a capacity of at least 990 litres.
Other factors such as the tank inlet flow rate and the usage patterns of the building should be taken into account; buildings with a poor rate of mains water supply will require greater storage. The siting of the break tank will also influence this. A tank on the ground floor of a building will fill at a higher rate than a tank on an upper floor or in the roof space. Siting a tank in the roof space of a building is likely to necessitate a larger storage volume.
The following graph shows the minimum storage required for a range of booster set peak flow rates: